UAV/Drone Lidar Mapping Basics
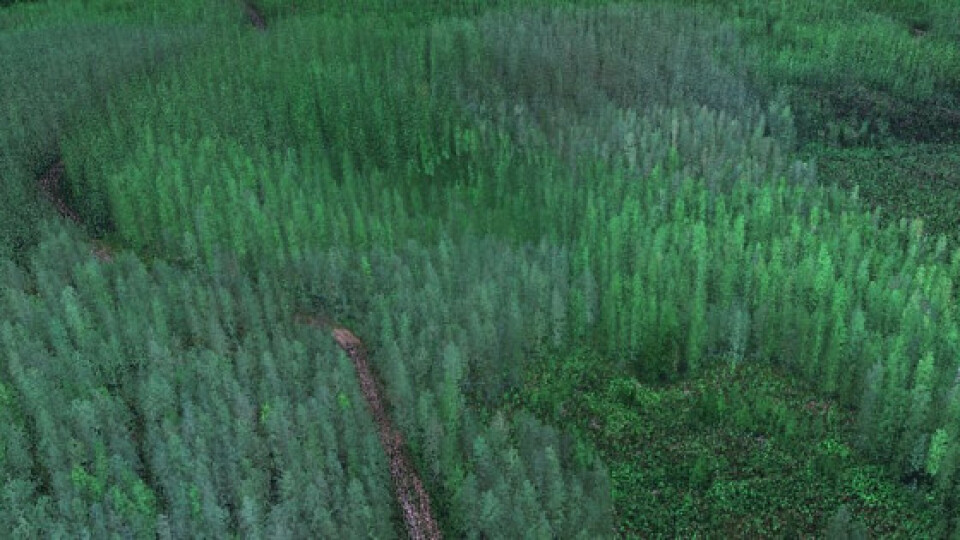
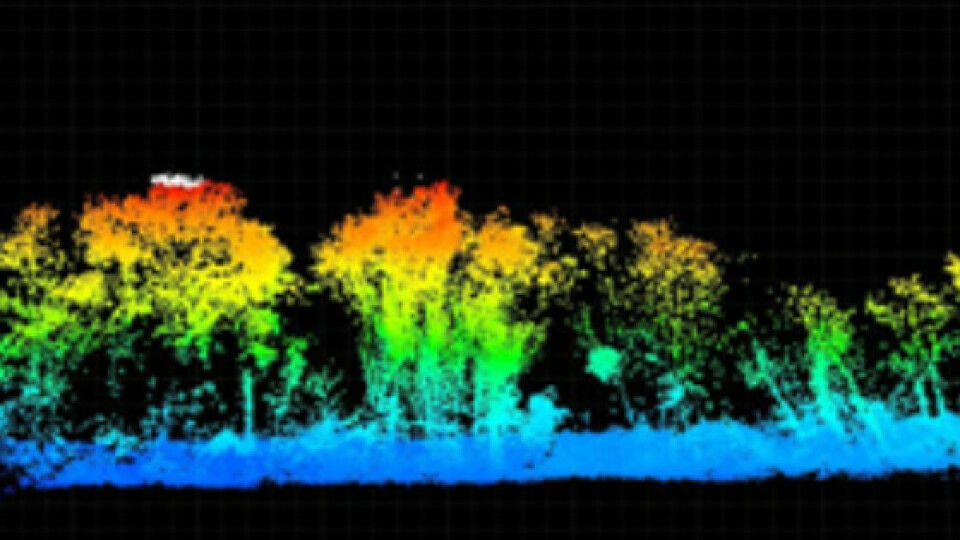
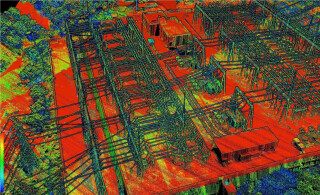
Light distance and ranging (LiDAR) technology has advanced tremendously in recent years and the valuable data it provides is highly sought after. Much like an echo where sound bounces off a wall, light reflects off of surfaces. LiDAR sensors are designed to send out pulses of concentrated light like a laser, then receive a return of that same pulse of light after it reflects off of a surface. The sensor can measure the time from when the pulse goes out and the reflection returns and the time passed can be used to calculate the distance between the LiDAR sensor and the object. In the case of aerial LiDAR mapping, this means you can use LiDAR to collect elevation data of the ground from an aircraft in order to create a digital terrain model.
For a thorough and visual representation of how LiDAR mapping technology works, check out this video from the National Ecological Observatory Network.
How Does LiDAR Remote Sensing Work? Light Detection and Ranging
When to use UAV/Drone Lidar compared to other 3D mapping techniques
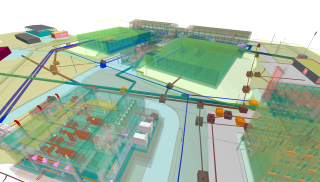
When it comes to geospatial applications that require 3D mapping of part of the Earth’s surface, there are many methods to create a digital terrain model including terrestrial mapping with GNSS or total stations, satellite or aerial photogrammetry, or LiDAR. Terrestrial mapping can produce very precise data products, but often the density of the 3D points collected is insufficient to accurately represent a surface. Certain areas may also be unsafe for operators to access or the labor may be too expensive for larger projects. Satellite or aerial photogrammetry can produce a higher density of 3D points, but these points do not always depict an accurate surface of the actual ground or bare earth. Cameras used in photogrammetry work flows do not penetrate tree canopy or other vegetation like LiDAR and therefore may be insufficient to produce accurate elevation data of a terrain.

UAV/Drone Lidar applications
LiDAR mapping is of tremendous benefit when a project requires accurate elevation data of highly-vegetated areas, large areas, or places that are difficult or unsafe to access on the ground. Applications include the following, among others:
- Environmental surveys for slope stability, cultural resources, forest roads, watershed analyisis
- Forestry for measuring tree heights, assessing stand health, and stratifying understory
- Land surveying for accurate digital terrain models
- Powerline inspections for vegetation encroachment, hazard analysis, tension, and construction monitoring
- Road and rail for project estimating of cut and fill, surface integrity analysis, and construction monitoring
hen to use UAV/drone Lidar?
While LiDAR mapping offers many benefits, tasking a manned aircraft or satellite for a project is often cost-prohibitive, weather-dependent, or incapable of meeting time constraints. This is where drone LiDAR makes good sense.

Related products