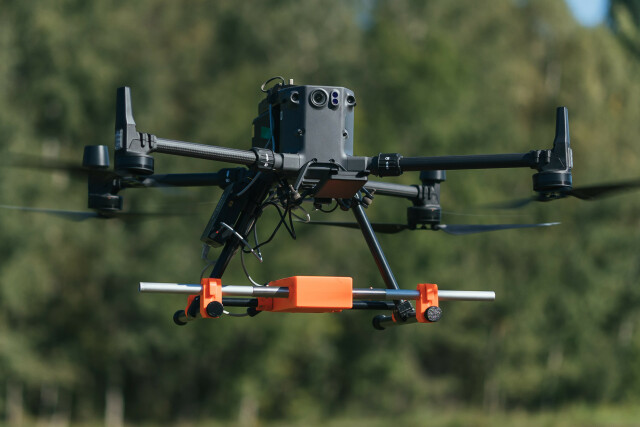
Zond Aero GPR systems for drones
Acquire Subsurface Data Quick, Safe and Efficient!
Drone-mounted GPR systems allow you to see through ground surfaces, ice, rocks and fresh water in unsafe and hazardous environments without compromising personnel safety, providing an additional solution for more efficient surveying.

Description
HOW IT WORKS
The system consists of a UAV integrated with a Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR). The system ensures complete integration by adding the SkyHub onboard computer. The drone's flight is planned and managed using the full functionality of UgCS universal ground control software.
UAV
DJI M350, M300, and M600 series of-the-shelf drones, as well as UAV's based Pixhawk autopilots with ArduCopter firmware (InspiredFlight IF1200A, WISPR Ranger Pro, etc.).
GPR
GPR selected based on the survey's goals.
The Zond Aero GPR series was designed for airborne use from the ground up and covers all possible applications of airborne GPR systems:
Zond Aero LF: Low frequency, extremely customizable GPR system in terms of available frequencies; it was tested with antennas ranging from 50 to 400 MHz, making it the most versatile system in our portfolio. By default, it comes with 3x sets of dipoles for the 300, 150, and 100 MHz. Dipoles for other frequencies are available by request.
Zond Aero 500: versatile system with a center frequency of 500 Mhz, ideal for scans up to 2m deep.
Zond Aero 1000: high-resolution GPR with center frequency 1000 Mhz, most suitable for depth up to 0.5m, snow, and ice profiling
SkyHub onboard computer
SkyHub is an onboard computer to enhance the capabilities of commercial-off-the-shelf UAVs and enable integration with diverse sensors.
GPR's data logging is started automatically and geotagged with GPS coordinates from the autopilot.
Data is stored in the standard SEG-Y format.
Altimeter
The system has a laser or radar altimeter for automatic True Terrain Follow (TTF) flight. Since GPRs require the antenna to be raised as low as possible above the surface, airborne GPRs without the ability to fly very low in automatic mode are useless toys.
SPH Engineering’s True Terrain Following system allows it to fly as low as 0.5m above the surface in fully automatic mode.
UgCS
Flight planning and control software display GPR's status data and current trace.
APPLICATIONS
SNOW AND ICE PROFILING
Snow and ice are ideal environments for GPR, especially drone-mounted GPR systems. Depending on the survey, various GPR systems can be used:
Zond Aero 1000: Recommended for freshwater ice profiling to ensure ice road safety and depth up to 4m for environmental studies.
Zond Aero 500: recommended for snow/ice scanning up to 15m.
Zond Aero LF: recommended for very deep scanning up to several hundred meters in glaciers.
SMALL OBJECTS DETECTION
Zond Aero 1000 GPR system is applicable to detect small objects with a diameter starting from 8cm and pipes/cables with a diameter starting from 3cm.
BATHYMETRY OF FRESH WATER
The GPR-drone integrated system enables measuring the depth of water or profiling the bottom of freshwater rivers, lakes, and ponds up to 15 meters in depth.
Benefits – possibility to do work even when the water is frozen or the surface of the water is partially covered with ice. Compared to bathymetry using a boat (equipped with echo sounders), the drone with a GPR provides better accuracy in following survey lines thanks to the built-in GPS and automated flight. Also, in most cases, a drone makes delivering the necessary equipment to the desired area much easier.
Recommended GPR system: Zond Aero LF.
GEOLOGICAL SURVEYS FOR LAYERS PROFILING
Strata profiling is a standard task that needs to be done before any serious area development or construction works. The standard technique is drilling dozens of holes or conducting a GPR survey on carts.
A drone-mounted GPR system delivers higher work productivity and enables safer work conditions for personnel in rough terrain.
GPR allows finding any potentially dangerous underground water streams or lakes.
The recommended GPR system is Zond Aero LF or Zond Aero 500.
MAPPING OF UNDERGROUND INFRASTRUCTURE
Mapping underground infrastructure is essential before starting any construction works on previously developed territories or when actual documentation and maps for underground infrastructure are missing.
Recommended GPR system: Zond Aero 500.
Do you have questions about this product?
- Questions about price, availability, and/or retailers
- Questions about technical specifications and usage
- Questions about suitability for your project or application
Specifications
-
Environment
-
Min. operation temperature [°C]
-20
Max. humidity [%]
96
Max. operation temperature [°C]
60
Max. wind speed [m/sec]
8
-
Battery and Power
-
Battery type
Drone main battery is used to provide power to the GPR using standard power socket of the drone intended for payload.
-
Imaging/scanning devices
-
Onboard imaging/scanning devices
Additional sensors
Build-in Stablilsation
Y
Exchangeable
Y
-
Platform
-
Platform
Copter
-
Operation Characteristics and Safety
-
Training provided
Y
Collision avoidance systems (CAS)
Y
Autonomous emergency landing
Y
Automatic launch and landing
Y
Min. ø of launch/landing site [m]
3
-
Dimensions
-
Weight of filled fuel tank [kg]
0
Transport on human back
N
-
Base Station
-
Ground computer included
N
Sensor control
Y
Real time image and video download link
Y
Type of Ground computer
Windows-based laptop
-
General
-
Year of last update
2024
Product Name
Zond Aero GPR - drone-mounted GPR series
-
Included software and automatically generated
-
Type of software included
Flight planning
Flight planning software
UgCS
Documents